Zoe KleinmanKnow-how editor
 BBC
BBCThere’s an outdated adage amongst tech journalists like me – you possibly can both clarify quantum precisely, or in a method that folks perceive, however you possibly can’t do each.
That is as a result of quantum mechanics – a wierd and partly theoretical department of physics – is a fiendishly troublesome idea to get your head round.
It includes tiny particles behaving in bizarre methods. And this odd exercise has opened up the potential of an entire new world of scientific tremendous energy.
Its mind-boggling complexity might be a consider why quantum has ended up with a decrease profile than tech’s present rockstar – synthetic intelligence (AI).
That is regardless of a gentle stream of current massive quantum bulletins from tech giants like Microsoft and Google amongst others.
Broadly talking, we have a tendency to consider quantum extra generally within the type of {hardware} like sensors and computer systems, whereas AI is extra software-based – it requires {hardware} to function.
Put them collectively, and we’d in the future have a brand new type of expertise that is extra highly effective than something now we have ever created… though the phrase “may” is doing a little heavy-lifting in that individual prediction, warns Brian Hopkins, VP and principal analyst in rising tech at analysis agency Forresters.
“The potential is there, however the jury continues to be out,” he says.
“Preliminary experiments recommend promise, however all of them point out that we require way more highly effective quantum computer systems and additional revolutionary analysis to successfully apply quantum results to AI.”
When it comes to their worth, each are profitable. The quantum sector may very well be value as much as $97bn (£74bn) by 2025, in keeping with market analysis group McKinsey.
In the meantime, AI’s worth is forecast within the trillions. However they each reside underneath the shadow of hype and the bursting of bubbles.
“I used to consider that quantum computing was the most-hyped expertise till the AI craze emerged,” jokes Mr Hopkins.
In mid-October analysts warned some key quantum shares might fall by as much as 62%, whereas mutterings about an AI bubble develop ever louder.
Quantum and AI have another factor in frequent – errors. Whereas we’re largely acquainted now with the “hallucinations” of generative AI instruments, quantum is affected by a special type of error.
These are brought on as a result of the state through which the particles must function is so fragile. The slightest change to the surroundings, together with gentle and noise, can disrupt them.
It is tough to maintain such an surroundings. This week Elon Musk steered on X that quantum computing would run greatest on the “completely shadowed craters of the moon”.
Quantum computer systems do not look something like a standard machines. There isn’t any design blueprint, however they’re at the moment very massive.
They exist in laboratories, and essentially the most generally adopted format appears to incorporate a type of jellyfish-inspired form.
They require extraordinarily chilly temperatures and lasers. It isn’t the kind of factor you are prone to have in your house, not to mention in your pocket.
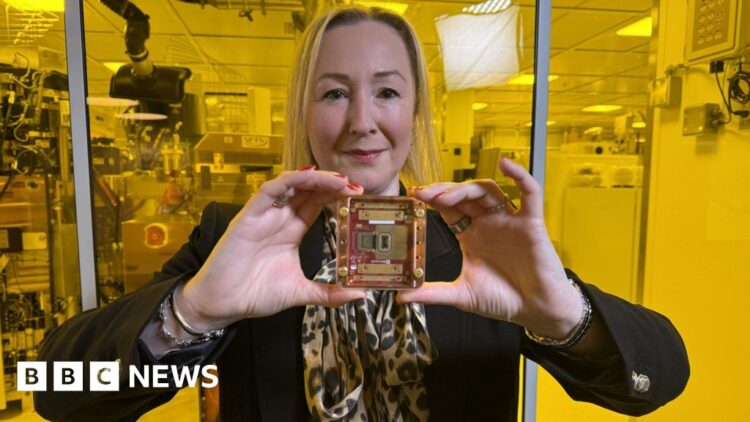
They’re additionally a bit bling – researchers have discovered that utilizing artificial diamonds to create qubits, that are the constructing blocks of quantum computer systems, allows them to work a lot nearer to room temperature.
The posh jeweller De Beers has a subsidiary firm referred to as Component 6, which claims to have launched the world’s first general-purpose quantum-grade diamond in 2020. And it has labored with Amazon Net Companies on optimising synthetic diamonds for future networks of quantum machines.
 AFP through Getty Pictures
AFP through Getty PicturesThese machines are all of their infancy proper now, there are believed to be round 200 of them in the entire world (China nevertheless has not disclosed what number of it has) – this does not cease quantum consultants making daring claims about their potential.
“We as shoppers will contact the impacts of quantum computing in virtually each stroll of our lives,” mentioned Rajeeb Hazra, the boss of Quantinuum, a agency lately valued at $10bn. He was speaking to the BBC’s Tech Life podcast.
“The realm of quantum computing is, in my thoughts, while you take a look at the functions, as massive if not larger than AI.”
Prof Sir Peter Knight is without doubt one of the UK’s prime quantum consultants. “Issues that would take the age of the universe to calculate, even on essentially the most highly effective supercomputer, may very well be carried out in all probability in seconds,” he informed Dr Jim Al-Khaleli on BBC Radio 4’s The Life Scientific.
So what precisely are these gigantic, life-changing issues that the machines may do as soon as they’re prepared?
As with AI, there’s a variety of quantum analysis directed in direction of bettering healthcare.
Quantum computer systems might in the future be capable of effortlessly churn by infinite mixtures of molecules to give you new medication and drugs – a course of that at the moment takes years and years utilizing classical computer systems.
To present you an concept of that scale – in December 2024, Google unveiled a brand new quantum chip referred to as Willow, which it claimed might take 5 minutes to unravel an issue that may at the moment take the world’s quickest tremendous computer systems 10 septillion years – or 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years – to finish.
Hazra says this might pave the best way for personalised treatment, the place as an alternative of getting a regular prescription, you get a selected drug tailormade to your particular person physique, that is most probably to give you the results you want.
And that applies to wider chemical processes too, similar to new methods to supply fertilizers extra effectively, probably an enormous increase for international farmers.
Quantum sensors, which use the ideas of quantum mechanics to measure issues extremely exactly, exist already and are present in atomic clocks.
In 2019, scientists at Nottingham College put them in a prototype gadget the scale of a motorcycle helmet, and used them in a brand new system to conduct non-intrusive mind scans on youngsters with circumstances similar to epilepsy.
“The foundations for human cognition are laid down within the first a long time of life, however there have all the time been restricted methods to check them attributable to restrictions in mind scanning expertise,” mentioned researcher Ryan Hill on the time.
“A selected downside has all the time been motion and the truth that the big conventional mounted scanners have all the time required sufferers to remain utterly nonetheless.
“Not solely does this fail to offer an correct image of the mind working in a pure surroundings, but it surely additionally locations extreme restrictions on who might be scanned, with youngsters representing the most important problem.”
 AFP through Getty Pictures
AFP through Getty PicturesFinal 12 months, scientists at Imperial Faculty, London trialled an alternative choice to GPS satellite tv for pc navigation, dubbed a “quantum compass”, on the town’s underground Tube community.
GPS does not work underground however this does – the concept is that it might extra precisely observe and pinpoint objects wherever on the earth, both above or beneath floor, not like GPS alerts which might be blocked, jammed and affected by the climate.
“The UK financial system depends on GPS to the tune of £1bn per day, place, navigation and timing – that is usually labelled a defence requirement – however all our monetary transactions require a timestamp for authentication,” says Dr Michael Cuthbert, director of the UK’s Nationwide Quantum Computing Centre.
“Utilizing quantum clocks, gyroscopes and magnetometers allows us to create a resilience towards jamming and spoofing of our very important navigational methods.”
The Nationwide Grid is investing in quantum analysis to see if it might probably assist with what’s referred to as “load shedding” – how you can maximise the output of 1000’s of mills from varied vitality sources as demand rises and falls in actual time, stopping blackouts.
And Airbus partnered with the UK quantum agency IonQ to trial quantum-based algorithms designed to load cargo extra effectively onto plane. An plane can use 1000’s of kilos of additional gas if its centre of gravity shifts by only a small quantity.
 AFP through Getty Pictures
AFP through Getty PicturesThus far, so good – however we additionally want to speak about secrets and techniques.
It’s broadly accepted that present types of encryption – the best way through which we retailer each private knowledge and official secrets and techniques – will in the future be busted by quantum expertise with the ability to churn by each single attainable mixture in file time, till the info turns into unscrambled.
Nations are identified to be already stealing encrypted knowledge from one another with a view to with the ability to decode it in the future.
“It is referred to as harvest now, decrypt later,” says Prof Alan Woodward, a cybersecurity professional from Surrey College.
“The speculation of how you can break present types of public key encryption await a really operational quantum laptop,” he provides.
“The menace is so excessive that it is assumed everybody must introduce quantum-resistant encryption now.”
The second a such a pc exists is usually known as Q-day. Estimates of when it would arrive fluctuate, however Brian Hopkins at Forrester says it may very well be quickly – across the 12 months 2030.
Firms like Apple and the safe messaging platform Sign have already rolled out what they consider to be post-quantum encryption keys, however they can’t be utilized retrospectively to present knowledge encrypted within the conventional method.
And that is already an issue. In October, Daniel Shiu, the previous head of cryptographic design at GCHQ, the UK’s intelligence, safety and cyber company, informed the Sunday Occasions it was “credible that the majority UK residents could have had knowledge compromised” in state-sponsored cyber assaults carried out by China – with that knowledge stockpiled for a time when it may be decrypted and studied.